Innovative Pedagogies

Explore Innovative Teaching Pedagogies With Us!
BAUHAUS4EU is developing a shared educational ecosystem that promotes sustainability, inclusiveness, creativity, and quality in higher education, in line with the New European Bauhaus and the European Education Area. As a living laboratory for educational innovation, the alliance supports transdisciplinary, learner-centred, and practice-oriented pedagogical approaches that respond to societal and educational transformation.
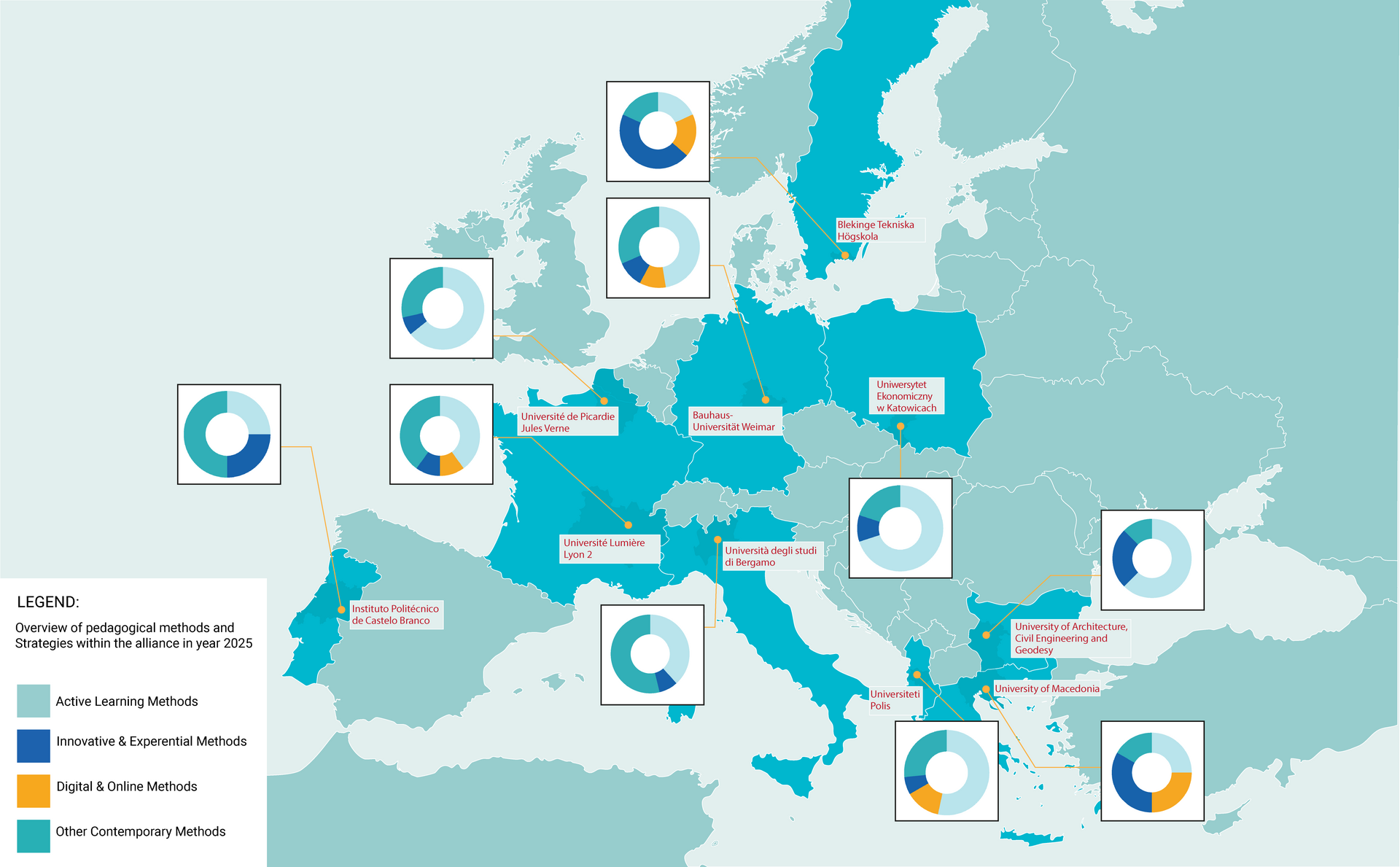
To support this goal, BAUHAUS4EU has developed a Map of Innovative Pedagogies through a structured and collaborative process involving all partner universities. Based on a shared conceptual framework, the mapping identifies, classifies, and compares innovative teaching and learning approaches currently implemented across the alliance. The results are documented in a dedicated report (MS 8 download link) and provide the analytical foundation for future alliance-level collaboration and exchange.
The map offers an overview of innovative pedagogical strategies and methods applied across partner institutions, supporting knowledge sharing and mutual learning within the BAUHAUS4EU alliance.
Explore the map below to discover innovative pedagogies across BAUHAUS4EU.
Brainstorming – Generating creative ideas as a group without judgment.
Case Study Analysis – Case studies invite students to consider real-world examples and examine issues from a diversity of stakeholder perspectives. Case studies can provide a detailed example of opportunities for students to engage in research with complex human-environment systems.
Concept Mapping – Visual diagrams showing relationships among concepts. Mind maps, cognitive maps and argument maps are all approaches for graphically representing relationships between ideas.
Debate – Structured argumentation on a specific topic between opposing sides.
Experiential Learning – Learning through direct experience and reflection. Experiential learning is an engaged learning process whereby students “learn by doing” and by reflecting on the experience. Experiential learning activities can include, but are not limited to, hands-on laboratory experiments, internships, practicums, field exercises, study abroad, undergraduate research and studio performances.
Fishbowl – Inner group discusses while outer group observes and reflects.
Flipped Classroom – Content learned at home, practice done in class. Flipped learning, sometimes called the "flipped classroom", is a pedagogical approach which uses time and space in a different way from the way courses are typically taught. In traditional instruction, students' first contact with new ideas happens in class, usually through direct instruction from the professor; after exposure to the basics, students are turned out of the classroom to tackle the most difficult tasks in learning — those that involve application, analysis, synthesis, and creativity — in their individual spaces. Flipped learning reverses this, by moving first contact with new concepts to the individual space and using the newly-expanded time in class for students to pursue difficult, higher-level tasks together, with the instructor as a guide.
Inquiry-Based Learning – Students pose questions, investigate, and construct understanding. Teachers offer support and guidance as students work on projects that depend on them taking on a more active and participatory role in their own learning. Different students might participate in different projects, developing their own questions and then conducting research — often using online resources — and then demonstrate the results of their work through self-made videos, web pages or formal presentations.
Jigsaw Method – Each student becomes an expert on one part and teaches others. The jigsaw model of instruction is a cooperative peer-learning method developed to help reduce racial tension in recently desegregated classrooms. Students are assigned to develop expertise on different sub-topics. Then students with expertise in each sub-topic are assembled to create a new ‘jigsaw’ learning team.
Minute Paper – Brief written response summarizing what was learned.
Peer Teaching – Students explain and teach concepts to each other.
Problem-Based Learning – Students learn through solving complex, real-world problems. Project-based learning and problem-based learning are broadly overlapping approaches to education, emphasizing the value of working on complex, real-world problems for students to develop knowledge, skills, and competences, particularly when the problems/projects represent interdisciplinary sustainability challenges. Problem-based learning may also overlap with case studies as another form of inquiry-based learning.
Project-Based Learning – Students work on a project over an extended period.
Role-Playing – Role play is a simulation technique in which students represent a situation, in a planned or spontaneous way. For it to be effective, it is important that there is “clarity of the content to be worked on and educational objectives established”.
Simulation – Imitating real-life processes for training or experimentation.
Student-Led Discussions – Students prepare and guide discussions on course topics.
Team-Based Learning – Collaborative learning in structured, permanent teams.
Think-Pair-Share – Individual thinking, paired discussion, and class sharing.
(Community) Service Learning – Combining learning objectives with community service. In community service learning, students engage in activities intended to directly benefit other people, where the activities are integrated with learning activities in an intentional and integrative way that benefits both the community organization and the educational institution.
Collaborative Writing – Groups of students writing and editing together.
Critical Pedagogy – Teaching with focus on awareness and emotional regulation.
Design Thinking – Creative problem-solving with empathy and prototyping.
Dialogic Teaching – Teaching through dialogue and open questioning.
Gamification (or game-based learning) – Incorporating game elements into the learning process. Gamification and game-based learning are similar in that both strategies promote engagement and sustained motivation in learning. In short, gamification applies game elements or a game framework to existing learning activities; game-based learning designs learning activities that are intrinsically game-like.
Hackathons – Intensive sessions solving problems or building projects collaboratively
Interactive Notebooks – Student journals combining notes, visuals, and reflections.
Learning by Teaching – Students learn content by preparing to teach it.
Learning Contracts – Agreements between instructor and student on goals and tasks.
Metacognitive Strategies – Teaching students to reflect on their own thinking.
Mindfulness Learning – Education aimed at understanding and challenging power structures.
Peer Assessment – Students evaluate each other's work.
Portfolio Assessment – Collection of student work showing growth and achievements.
Scaffolded Learning Gradual release of responsibility to the learner.
Storytelling (and digital storytelling) Using narratives to teach concepts and engage learners, also using digital tools.
Asynchronous Learning – Students learn on their own time with pre-prepared content.
Blended Learning – Combining face-to-face and online instruction. This method relies heavily on technology, with part of the instruction taking place online and part in the classroom via a more traditional approach, often leveraging elements of the flipped classroom approach detailed above. At the heart of blended learning is a philosophy of taking the time to understand each student’s learning style and develop strategies to teach to every learner, by building flexibility and choice into your curriculum.
Gamified Platforms – Using game-like systems to motivate learning.
Learning Management Systems (or cloud computing) – Platforms to organize and deliver course materials online.
Mobile Learning – Learning via smartphones or tablets on-the-go.
MOOCs – Massive online courses accessible to large audiences.
Podcast-Based Instruction – Using audio content to deliver educational material. Podcasts are audio episodes that focus on a specific theme or topic and can be accessed for free online.
Social Media-Based Learning – Using platforms like Twitter or Facebook for interaction. Social media are used in education internationally with the aim of: increasing student engagement in the educational process; enhancing peer learning; increasing student satisfaction and enjoyment from their participation; offering learners a simple, friendly, practical and easy-to-use learning environment; providing an easy-to-use tool for searching for current, up-to-date and innovative content.
Synchronous Online Teaching – Real-time virtual instruction via online platforms. Synchronous learning tools provide a virtual learning environment for students and allow for live classroom collaboration for distance learners. During a real-time, online lesson, the instructor and students meet via web-conferencing tools at scheduled days and times. Instructors and students share information, ideas and learning experiences in a virtual course environment. Synchronous sessions allow you to check in with your students on a regular basis.
Video-Based Learning – Educational content delivered through video.
Virtual Labs – Online simulations of laboratory experiments.
Webinars – Online seminars typically involving expert presentations.
Augmented Reality Learning – Enhancing real-world settings with digital information.
Challenge-based learning – Challenge-based learning (CBL) is a structured approach to using challenges in education or training. It consists of three stages: Engage, Investigate, and Act, and it is based on the idea that challenges ‘provoke’ learners into active participation and produce an outcome. CBL builds on experiential and constructivist learning, allowing participants to become both teachers and learners.
Choice Boards – Students choose from a set of learning activities.
Collaborative Problem Solving – Students work together to solve complex issues.
Contract Grading – Students agree to grading criteria and expectations.
Cooperative Learning – Structured group work with shared goals. Collaboration presupposes that the actors work on an equal and mutual basis, in order to deepen their knowledge in a reciprocal manner. Collaboration also requires joint decision-making, the promotion of dialogue, sharing and mutual learning.
Crossover Learning – Connecting formal and informal learning environments.
Educational Games – Games designed specifically to support learning objectives.
ePortfolios – Digital portfolios showcasing student work and progress.
Field Trips – Off-campus visits that enhance experiential learning.
Group work – Group work plays an important role in the classroom, as it creates the opportunity for dialogue and exchange of information. In this dynamic of work, the student interacts, analyses, questions, argues, justifies and evaluates.
Inter-disciplinary team teaching – Team-taught courses allow for the possibility of having specialists in different fields help students explore interdisciplinary and transdisciplinary topics from two or more distinctive disciplinary perspectives
Learning Circles – Collaborative groups engaging in dialogue around topics. Supply Chain Analysis or Life Cycle Assessment activities challenge students to consider sustainability through the lens of a specific product or commodity, understanding its economic, social, and environmental backgrounds, contexts, and effects.
Open Educational Resources – Use of freely accessible, openly licensed materials.
Pop Quizzes – Unannounced quizzes to encourage consistent study habits.
Reflective Journals – Students write reflections on what and how they learn.
Self-Assessment – Students evaluate their own learning and performance.
Service Projects – Community-focused projects integrated with academic content.
Virtual Reality Learning – Immersive environments to simulate learning contexts.
Work-Based Learning – Learning that takes place in a professional setting.
Stay Tuned!
Listen to our BAUHAUS4EU Podcast and sign up for our newsletter – stay up to date on all of our ongoing developments and planned activities!
Download Area
In the Download Area, you can find our communication kit, logos, deliverables and other useful documents.